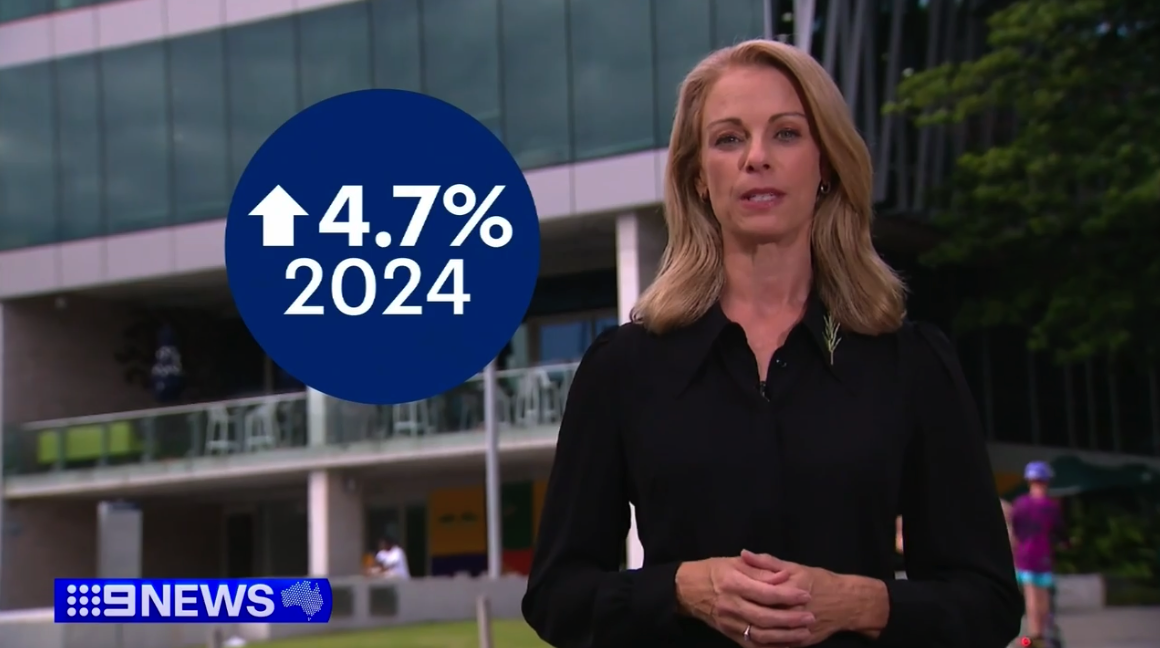
Recent data indicates a nearly 5% rise in HECS debts for the new financial year, amounting to an average increase of $1000 per student debt. This follows a 7.1% increase in HECS debt last year. With two consecutive years of growth, borrowers with HECS debt are likely to feel the impact. However, securing a loan is still achievable.
Securing a mortgage loan signifies a pivotal step towards achieving homeownership and financial stability for many individuals. However, navigating the mortgage landscape becomes intricate, particularly for those carrying HECS (Higher Education Contribution Scheme) debts. Despite being invaluable investments in education, HECS debts can unexpectedly affect credit scores and borrowing power. In this guide, we’ll unravel the complexities surrounding mortgage loans and delve into the impact of HECS debts on your ability to secure financing and realize your homeownership aspirations.
Understanding HECS Debts:
HECS debts represent a common financial obligation for numerous Australians who pursued higher education. This government-backed loan scheme enables students to defer university costs until they surpass a specific income threshold. While facilitating access to education, HECS debts wield significant financial implications, extending to mortgage applications and other facets of personal finance.
Impact on Credit Scores:
A crucial determinant of mortgage loan eligibility and terms is your credit score. HECS debts, akin to other forms of debt, factor into credit score calculations. Although HECS debts may not directly diminish credit scores, they can indirectly influence borrowing capacity, impacting creditworthiness. Lenders assess debt obligations when evaluating mortgage applications, potentially constraining borrowing limits and affecting credit scores if debt-to-income ratios are exceeded.
Borrowing Power Considerations:
Lenders scrutinise income, expenses, and existing debts when assessing mortgage eligibility. HECS debts are integral to this financial evaluation, influencing borrowing power. Higher HECS debts may elevate debt-to-income ratios, diminishing borrowing capacity or altering loan types and terms. Additionally, lenders may impose stringent criteria or higher interest rates for borrowers with substantial HECS debts, reflecting perceived risks associated with heightened debt levels.
Strategies for Managing HECS Debts and Mortgage Applications:
Mitigating the impact of HECS debts on mortgage applications necessitates strategic approaches:
Pay down existing debts: Prioritise settling high-interest debts, including HECS obligations, to bolster debt-to-income ratios and augment borrowing potential.
Improve credit scores: Practise sound financial habits, such as timely payments, to elevate credit scores and show creditworthiness to lenders.
Explore debt consolidation: Investigate consolidating debts, including HECS obligations, into a unified loan with favourable terms, potentially enhancing financial profiles and borrowing capacities.
Seek expert advice: As mortgage brokers, Go Mortgage can help to navigate mortgage options, tailoring strategies to manage HECS debts and attain homeownership goals.
Don’t miss out on our podcast for valuable insights, tips, and tricks on mortgage loans, as well as how our dedicated brokers and team can support you.
Conclusion:
HECS debts wield significant influence on credit scores and borrowing power during mortgage applications. Particularly given the levels of inflation we have experienced over the last two years. By comprehending how lenders assess HECS debts and implementing proactive strategies, we can help you optimise your prospects of securing a mortgage loan and getting into the house of your dreams.
Further information